Ever since we have got into fitness we get ourselves more conscious towards the name called fats. Many of us skip meals, perform diurnal fasting and many of us really go through a systematic way to maintain balance between fat loss and muscle gain the way it should be.
In this particular article we have brought you to know about whats and hows of different types of fat molecules, we will get to know how different types of fats affect our body internally and externally and their sources.
ADVERTISEMENT

There are two types of fats saturated fats and unsaturated fats.
Saturated fats
Let’s understand first from a chemical standpoint. Fatty acids are made up of long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Some carbon atoms are linked by single bond and others by double bonds. In saturated fat, all the carbon atoms are saturated with hydrogen atoms and do not contain double bonds between the carbon atoms. This is because they have linear formation.
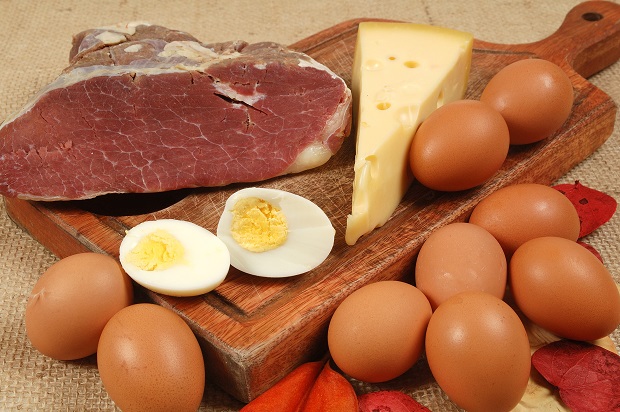
Bonds in saturated fats is similar to the the building made of solid bricks. These bonds are often solid at room temperature like butter. It is like a fat which is inside or around meat. Saturated fats are mostly found in animals like pork, beef and chicken. Egg yolk, palm oil, cheese, coconut oil also have saturated fat in it. Saturated fats are less found in leaner animal products i.e. pork loin, chicken breast.

Are saturated fats healthy?
Saturated fats are considered as a bad fat. Researchers found that eating saturated fats increases the level of cholesterol in the blood stream. This was an important finding because they also knew that having high cholesterol was linked to increased heart disease risk. It affects the cholesterol level. It increases overall LDL cholesterol and also increases HDL cholesterol. it can also increase LDL particle size.
ADVERTISEMENT
There is a evidence that replacing saturated fats with good unsaturated fats can help lower LDL cholesterol. The American Heart Association recommends aiming for a dietary pattern that achieves 5% to 6% of calories from saturated fats and that is about 13 grams of saturated fat per day.
Unsaturated fats
Unsaturated fats have 3 sub types:
1. Trans fats
2. Monounsaturated fats
3. Polyunsaturated fats
Unsaturated fats have at least one double bonded set of carbon atoms in their structure. These bonds are like chains that can bend, move and flow. These bonds are loose bonds so at room temperature these fats are mostly liquids. So oils have mostly unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats mostly comes from plants example nuts, seeds, but there are few products like coconut oil, palm oil, milk they are liquid at room temperature but are high in saturated fats.

Trans fats are solid at room temperature. There are two types of trans fats found in foods.
i. Naturally occurring trans fats
Dairy products have about 2 to 5% of trans fat from total fat and it is about 3-9% of fat in beef and lamb. According to several researches the moderate intake of trans fat does not cause harmful affects.
ADVERTISEMENT
ii. Artificial trans fats
Artificial trans fats are created in industries. They are made when liquid oils are turned into solid fats through a process called hydrogenation. Hydrogenation increases the flavor and life of foods.
In November 2013, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) concluded that partially hydrogenated oils are no longer recognized as safe in human food.
Companies use trans fats because it is inexpensive and give desirable taste and texture. Many restaurants use trans fats to deep fry foods because if oil mixed with trans fats can be used many times for frying.
Many countries like Switzerland, Canada ,Denmark have restricted the use of trans fat in food service. You can spot trans fat by looking for the ingredients referred to as “partially hydrogenated oils” on the packing
ADVERTISEMENT
How trans fat affects the body?
- Raise bad cholesterol (LDL).
- Lowers good cholesterol (HDL).
- Causes risk of developing heart disease.
- Increase the risk of development of type 2 diabetes.
- Increase risk of colon cancer.
Monounsaturated fats fats have only one carbon bond in their molecule. They are usually liquid at room temperature but they start to get solid when chilled.
According to AHA, it is a dietary fat and considered as a good fa t,but it doesn’t mean that we can consume this fat as much as we can. It is always about moderation. Any fat can be unhealthy if consumed in high quantity.
Olive oil is the best source of monounsaturated fats. Other sources of monounsaturated fats are: avocados, nuts,canola oil, sesame oil, peanut oil.
How monounsaturated fats affects the body?
- Lowers bad cholesterol level in the blood.
- Lower the risk of heart disease.
- Olive oil contains vitamin E in it which is good for skin and hair.
Polyunsaturated fats have more than one unsaturated carbon bond. they usually remain liquid at room temperature but same as mono start to turn solid when chilled.
ADVERTISEMENT
Polyunsaturated fats are classified by their omega numbering. Omega carbon is the carbon atom which is present at the end of the hydrocarbon chain.
There are 4 types of omega fatty acids, which are determined by the location of first double bonded carbon atom.
i. Omega 3
ii. Omega 6
iii. Omega 7
iv. Omega 9
Out of these four, omega 7 and omega 9 are produced in the body so there is no need to consume these fatty acids. Our bodies do not make omega 3 and 6, so we can get them from food.
ADVERTISEMENT
Omega 3
They are considered as a good fat.
The three omega 3’s which are found in food are:
i. Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA): This is plant based omega 3. This is found in green leafy vegetables, chia seeds, canola and flax seeds, soya bean, walnut, almonds.
ii. Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): it is found in oily fish, algae oil and krill oil.
ADVERTISEMENT
iii. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): this is also found in oily fish, krill oil and algae oil. Our body convert some DHA molecules back to EPA in order to keep them at equal levels if we consume more DHA.
How omega 3 affects our body?
- Lowers high triglycerides.
- Regulates cholesterol.
- Lowers high blood pressure.
- Prevents plaque build up.
- Reduces metabolic syndrome symptoms.
- Prevents blood clots.
- Fights against depression.
- Reduces inflammation.
- Lowers cancer risk.
- Improves sleep quality.
- Fights menstrual pain.
- Supports healthy skin.
- Control blood sugar.
Omega 6
These are type of fatty acids which we can get only from food or supplements.
There are 3 types of omega 6 fatty acids:
i. Linoleic Acid: This is found in soybean oil, corn oil, peanut oil, cottonseed oil.
ADVERTISEMENT
ii. Arachidonic Acid: This is found in meat, eggs, dairy products,peanut oil.
iii. GLA: This is found in borage oil, black currant seed oil, hemp seeds.
How Omega 6 affects our body:
- Helps reduce nerve pain.
- Fights inflammation.
- Treats arthritis.
- Supports bone health.
- Lowers high blood pressure.
- Lowers risk of heart disease.
Choose your fat intake wisely.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT